洛谷P2412题解:后缀树高效解决字符串比较问题

一、题目解读
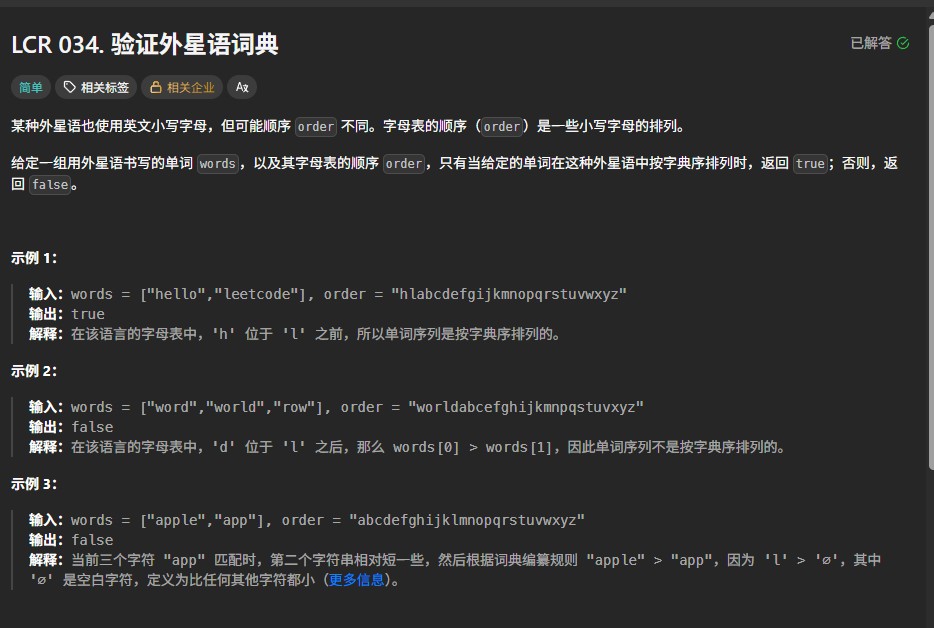
洛谷P2412题要求处理一组字符串,并支持区间内字典序最小字符串的查询。题目关键在于高效处理字符串比较与查找,传统暴力方法时间复杂度无法满足需求,需引入更优的数据结构。
二、解题思路
1. 预处理:将输入字符串转为小写,避免重复字符转换,减少比较开销。
2. 构建ST表:利用倍增思想,通过logN级预处理,保存每个区间的最小值索引。
3. 查询优化:利用二分查找原理,通过ST表快速定位区间内字典序最小的字符串索引。
三、解题步骤
1. 输入处理:读取N个字符串,存储原版与预处理小写版本。
2. ST表构建:
○ 初始化第一层级(log2(N)级):直接记录每个位置的原索引。
○ 递进层级:通过比较相邻区间的字典序最小值,合并生成更高层索引。
3. 查询实现:
○ 计算查询区间长度对应的ST层级j。
○ 比较区间两端对应层级的最小值,返回字典序更小者。
四、代码与注释
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; // 构建后缀树(ST表) vector<vector<int>> buildST(const vector<string>& words) { int n = words.size(); int k = log2(n) + 1; // 层级数量 vector<vector<int>> st(n, vector<int>(k)); // 存储各层级区间最小值索引 // 预处理小写版本避免重复转换 vector<string> lower_words(n); for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { lower_words[i].resize(words[i].size()); transform(words[i].begin(), words[i].end(), lower_words[i].begin(), ::tolower); } // 初始化第一层级(每个位置即为自身最小值) for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) st[i][0] = i; // 递进构建高层级 for(int j = 1; (1<<j) <= n; ++j) { // 遍历层级 for(int i = 0; i + (1<<j) - 1 < n; ++i) { // 遍历起始位置 int x = st[i][j-1], y = st[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]; // 比较两个子区间的最小值(考虑字典序相同则取索引小者) st[i][j] = (lower_words[x] > lower_words[y] || (lower_words[x] == lower_words[y] && x > y))? x : y; } } return st; } // 查询区间字典序最小值索引 int query(const vector<vector<int>>& st, const vector<string>& words, const vector<string>& lower_words, int l, int r) { int len = r - l + 1; int j = log2(len); // 对应层级 int x = st[l][j], y = st[r - (1<<j) + 1][j]; return (lower_words[x] > lower_words[y] || (lower_words[x] == lower_words[y] && x > y))? x : y; } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; // 输入字符串数量与查询次数 vector<string> words(n); for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) cin >> words[i]; auto st = buildST(words); vector<string> lower_words(n); for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { lower_words[i].resize(words[i].size()); transform(words[i].begin(), words[i].end(), lower_words[i].begin(), ::tolower); } while(m--) { int x, y; cin >> x >> y; x--; y--; int pos = query(st, words, lower_words, x, y); cout << words[pos] << '\n'; } return 0; }
五、总结
本解法通过后缀树(ST表)将区间查询优化至O(logN),结合预处理与二分思想,显著降低时间复杂度。适用于需频繁查询区间最值的场景,代码中细节(如小写预处理、字典序比较逻辑)体现了优化技巧,为同类问题提供高效解决方案。
原创内容 转载请注明出处